AI is changing the way software is created and maintained. It can handle repetitive coding, speed up testing, and detect errors early. Developers use it to predict problems, suggest improvements, and shorten release cycles.
AI in software development also helps teams understand user behavior by finding patterns in usage. It works alongside human skills, allowing developers to focus on complex tasks and meaningful features. This mix of speed, accuracy, and better decision-making makes AI a practical tool for modern software projects.

Advantages of AI in Software Development
A lot of software work isn’t exciting. There’s the long testing, fixing small things over and over, and checking the same sections of code for mistakes. An AI automation agency can help with that. Not in the “let’s build the whole app for you” way people sometimes imagine, but in small, steady ways that save time. It’s like giving part of the job to someone who never gets tired of the boring parts:
- Faster development. Some AI tools can write sections of code, run tests in the background, and spot bugs before they grow into bigger issues. This means a project can move forward without as many pauses.
- Better accuracy. Finding mistakes early is cheaper and simpler. AI in software development can pick up errors at the start, so teams do not have to spend weeks fixing them later.
- Time for real work. When the routine parts are handled, developers can focus on things that need human judgment. Building features, improving designs, or fixing unusual problems take priority.
- Spotting trouble before it starts. Looking at patterns in code and how users behave, AI can hint where something might go wrong. That gives teams a chance to adjust before it becomes a bigger task.
- Making it easier for users. AI can suggest changes based on how people actually use the software. Sometimes it is a small tweak to the interface, sometimes a better layout. Little changes can improve the way a program feels.
- Keeping watch after release. Once the software is live, AI can keep an eye on speed, errors, and security issues. It is like having a quiet monitor that does not get tired.
- Handling more without slowing down. Large projects bring more code and more moving parts. AI can help track tasks and keep them in order, so teams are not buried under the workload.
Using AI in software development is more like an extra set of hands than a replacement. It takes over the slower, heavier parts so the main work can move forward.
How to Use AI in Software Development
AI for software development can’t take the whole job off your hands, but it can take some of that load. It’s starting to appear in tools people already use. Sometimes you don’t even notice it’s there until it catches something you missed.
1. Automated Code Generation
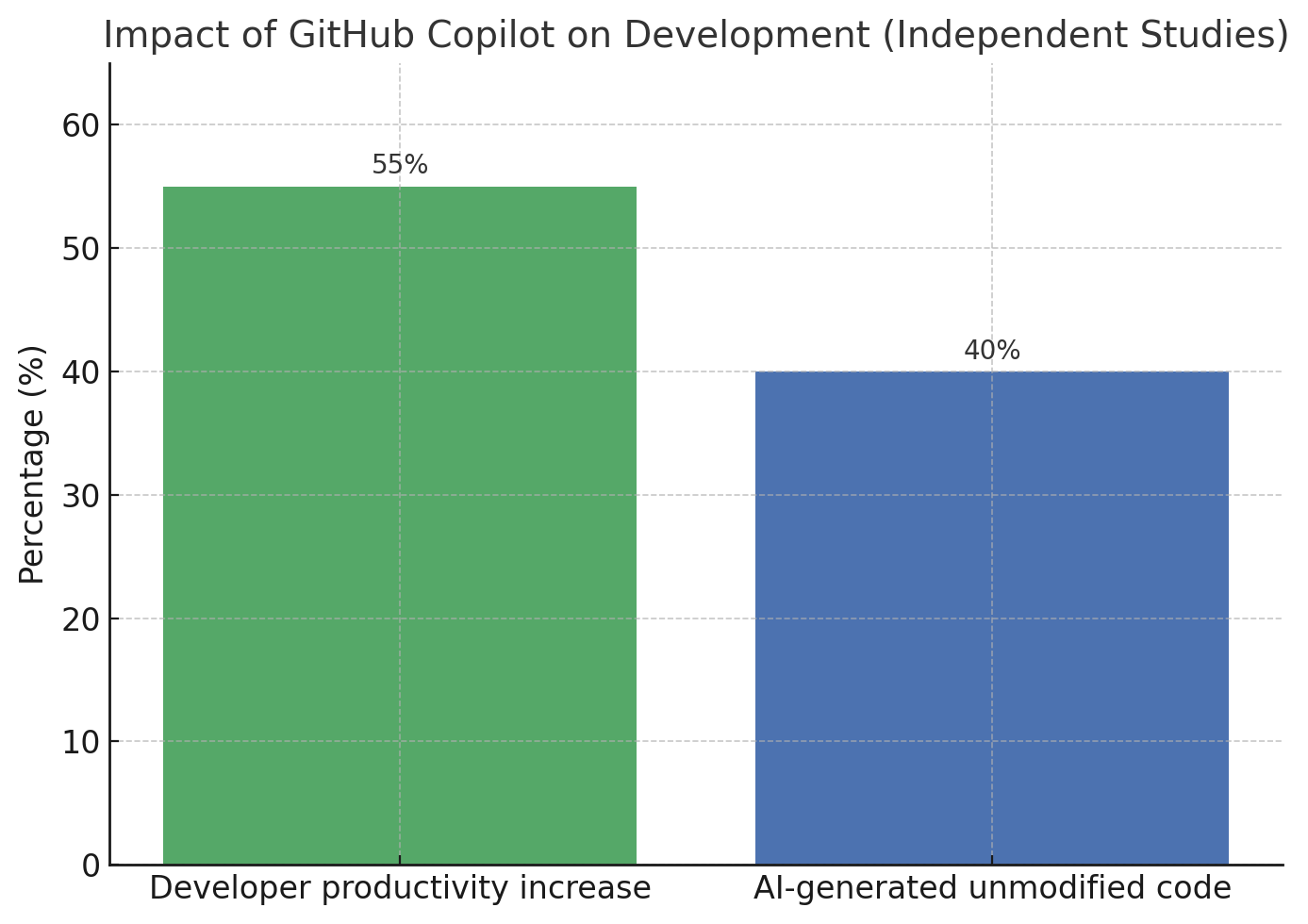
Blank files can be a momentum killer. About 40% of code is now generated by AI. AI, with the help of openai api integration, can give you something to work from: a rough template, a stub for a function, even filler data so you can check layouts before the real stuff is ready. It’s not perfect. Sometimes the logic is off, or it’s written in a style you wouldn’t normally use. But fixing that is still faster than starting from nothing.
Advantages:
- Saves time in initial setup.
- Lowers risk of typing errors in repeated code.
- Makes prototypes quicker to build.
The graph shows the impact of GitHub Copilot, an AI coding tool, on developer productivity and the share of code it helps create:
2. Code Review and Error Detection
Finding bugs by reading line after line is tiring and easy to get wrong. AI review tools can go through the code quickly, mark areas that might break, and flag security risks. They can also compare new changes to previous versions and point out anything unusual.
This is not a replacement for peer review, but it catches issues that might be overlooked, especially in large projects where no one person sees all the code.
Advantages:
- Early detection of risky code.
- Keeps quality more consistent.
- Works well for large codebases.
3. Test Automation
Every new feature can cause something else to break. Testing is one of those things no one wants to skimp on, but also no one’s excited to do. Artificial intelligence in software development can build and run tests automatically. You can be working on something else while it’s checking that yesterday’s change didn’t break the login form.
Advantages:
- Shortens testing cycles.
- Frees developers from repetitive test runs.
- Reduces the chance of unnoticed failures.
4. Predictive Maintenance
Some software problems give warnings before they cause damage. Slower response times, higher error rates, and unusual system behavior can all be signs of trouble ahead. AI for software development can spot these patterns and warn the team.
This works best in systems that need to run constantly, like payment processing or large online platforms. By fixing issues early, the team avoids downtime and keeps users from being affected.
Advantages:
- Reduces surprise outages.
- Cuts the cost of emergency fixes.
- Improves stability over time.
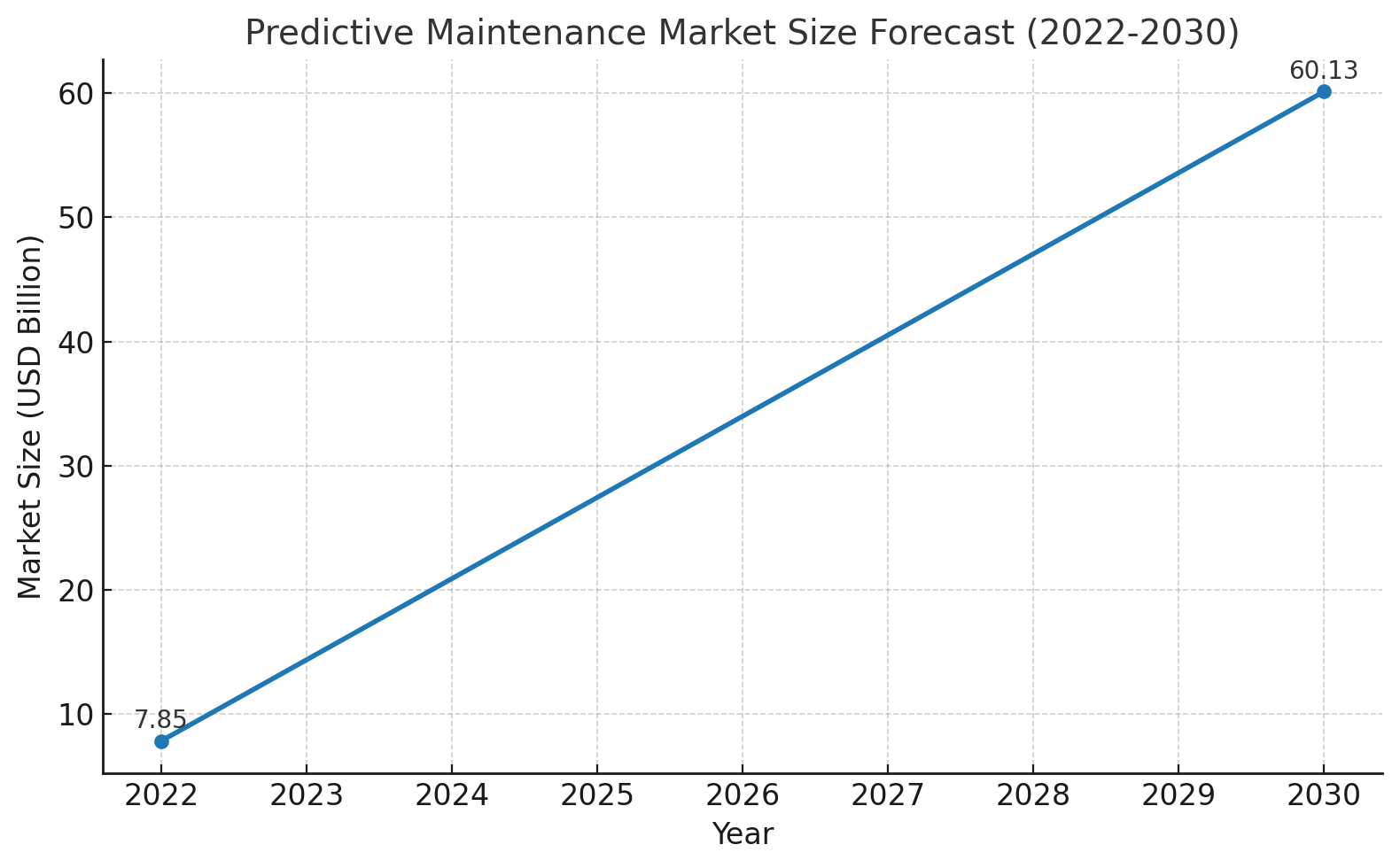
The predictive maintenance market is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years.
5. Improving User Experience
Users are unpredictable. They skip steps, get lost in menus, and abandon a task halfway. AI-powered software development can track all that. It might be noticed that people always drop out at the same point in a form, or that no one uses a feature you thought was important. Sometimes the answer’s obvious: shorten the form. Sometimes it’s not, and you have to dig.
Advantages:
- Highlights problem areas for users.
- Suggests improvements from real behaviour.
- Can lower the number of support requests.
6. Natural Language Processing for Interfaces
Not all users want to learn command formats or menu paths. With natural language processing, software can understand plain text or voice instructions. This can make search features, chatbots, and digital assistants more useful.
For example, instead of searching manually for a setting, the user can type “change password” and be taken straight to it. This lowers the barrier for less technical users and speeds up common actions for everyone.
Advantages:
- Easier for new or casual users.
- Speeds up navigation.
- Makes some tasks more accessible.
7. Project Management Support
Large projects have many moving parts, and deadlines can slip without warning. Artificial intelligence in software development can help by tracking progress, comparing it to past projects, and pointing out when a task is likely to be late. It can also suggest shifting work between team members to avoid bottlenecks.
This is not about replacing a project manager. It is more like having an extra set of eyes on the schedule, flagging small delays before they turn into big ones.
Advantages:
- Gives early warning on delays.
- Helps keep workloads balanced.
- Keeps schedules realistic.
8. Security Monitoring
Security problems often start small, with odd patterns of activity. AI-based software development can watch for these patterns in real time, spotting things like multiple failed logins, unusual file changes, or unexpected network traffic.
By catching them early, teams can respond faster and limit any damage. This is especially important for software handling sensitive data, where even a short delay can cause serious problems.
Advantages:
- Continuous monitoring without breaks.
- Detects threats faster than manual checks.
- Adds an extra layer of defence.
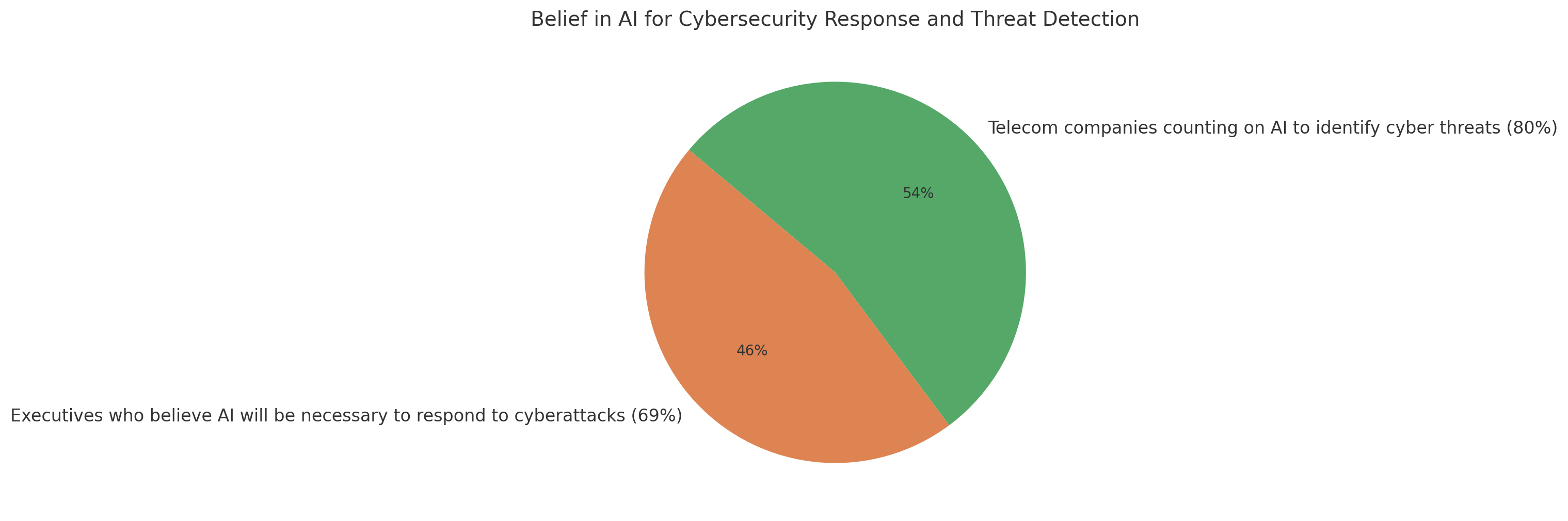
The graph highlights how strongly businesses see AI as part of their future cybersecurity plans:
AI in software development works best as a background partner. It is there to handle the slower, repetitive parts, find small problems before they grow, and make it easier to keep projects moving. The big ideas, complex fixes, and design choices remain in human hands. AI-powered software development just makes it easier for those hands to focus on what matters.
The Future of AI in Software Development
AI-driven software development is already part of how many teams write, test, and maintain software, but its role is likely to change further. The future will probably see tools that are more adaptable and more deeply connected to the way developers work. Some ideas are still only possible in theory, but they show where things might go.
Possible future changes:
- Artificial intelligence application development can design whole application architectures based on a short description, producing a working structure ready for human review.
- Development tools that adjust their interface and features in real time to match the habits and skills of the person using them.
- Artificial intelligence in software that follows a project from start to finish, remembering every change and giving advice based on the project’s entire history.
- Testing systems that not only check for bugs but also suggest new features based on how users interact with early versions.
- Security tools that simulate complex attack scenarios before code is released, giving teams a chance to patch weaknesses earlier.
- AI project managers that can automatically plan, assign, and reassign tasks while predicting team workload weeks ahead.
- Interfaces that allow direct spoken collaboration between multiple human developers and AI in the same environment.
- AI-driven code libraries that update themselves when better or safer methods are discovered.
These changes are not here yet, but they could reshape how software is planned and built. Programmers using AI tools will have more ways to focus on creative and complex work while leaving more routine tasks to machines.
