A mobile application platform is a group of tools and services that helps developers create, test, and run apps on phones and tablets. It covers the main steps of development, from writing code and building the interface to releasing the app on different systems.
Most platforms work for both iOS and Android, so one project can reach many devices. They also come with testing options, security settings, and ways to connect apps with outside systems. Using such a platform to develop mobile applications makes it easier for teams to work faster and avoid mistakes while keeping the app stable on different devices. In simple terms, it gives the base needed to build and manage mobile applications from start to finish.
Best Mobile App Development Platform
Statista reports that the global mobile app market is expected to grow to 756 billion dollars by 2027, rising at an average annual rate of 8.58% between 2022 and 2027.
Building mobile applications requires more than just writing code. Developers need a base that gives them tools for coding, testing, and publishing apps in one place. A mobile app backend development helps with this work by offering ready features, integrations, and support for different systems. With so many choices available, it can be hard to decide which mobile app platforms fit best. Below are six of the most trusted options. Each has its own style, advantages, and limits, but all of them are strong enough to create modern mobile applications.
1. React Native
React Native is an open-source framework created by Facebook. It allows developers to build mobile apps using JavaScript and React. The main strength of React Native is the ability to write one codebase that works on both iOS and Android.

Who It Suits
React Native fits companies that need efficiency and faster release cycles. Startups often choose it because they can bring their product to market faster without hiring separate teams for each platform. Small and mid-sized companies also benefit because they can reduce costs while still reaching a wide audience. Development teams with a background in JavaScript find it easier to adapt to React Native, which lowers the learning curve compared to platforms that require less familiar languages.
Pros
- One shared codebase works for iOS and Android
- Large support community with many ready-to-use libraries
- Performance that can be close to native applications
- Hot reloading and live reloading make development quicker
Cons
- Some advanced features still need native coding in Swift, Java, or Kotlin
- Updates can cause issues with existing packages and require fixes
- Apps with heavy graphics or advanced animations may run more slowly
React Native stands as a practical solution for many projects. It offers a balance between mobile app development speed, cost, and performance. While it may not be the best option for very demanding applications like high-end games, it remains a strong and dependable choice for most business and consumer apps.
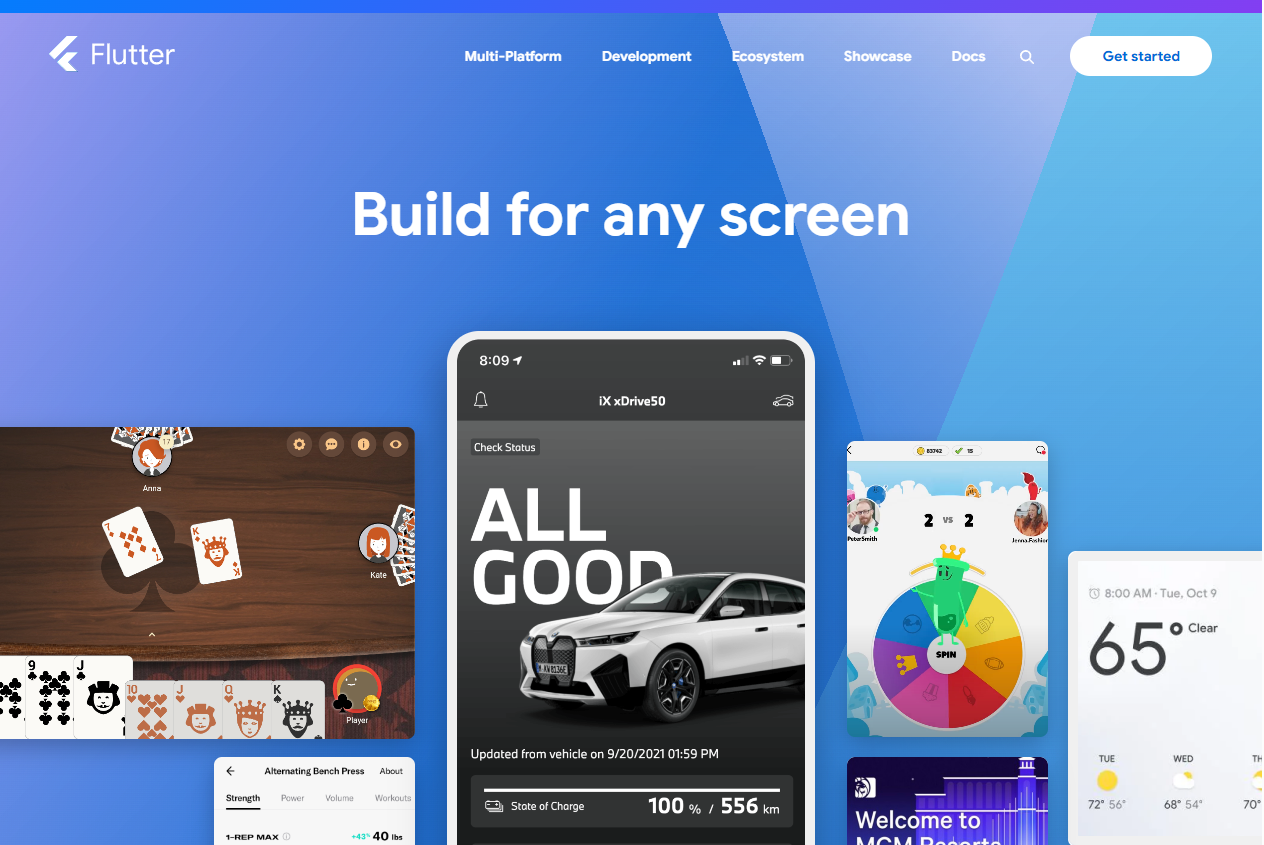
2. Flutter
Flutter is developed by Google and uses the Dart programming language. It is known for its fast performance and rich user interface options. With Flutter, apps run smoothly across platforms and look consistent.
Who It Suits
Flutter is a well-suited mobile app platform for projects where design and user experience are important. Startups often choose it to bring polished apps to market quickly without hiring large teams. E-commerce companies also see value in Flutter app development because it allows them to create visually appealing apps that can run on both iOS and Android with a single codebase. Developers who want complete control over both design and performance find Flutter a strong option, especially if they are willing to invest time in learning Dart.
Pros
- Delivers high performance with near-native speed
- One codebase can serve multiple platforms, including web and desktop in addition to mobile
- Wide library of customizable UI widgets
- Supported and updated by Google, with strong community growth
Cons
- Dart is less widely known compared to languages like JavaScript, which can make hiring harder
- Apps built with Flutter often have larger file sizes
- The ecosystem of third-party libraries is still smaller compared to older frameworks
Flutter provides a flexible and reliable foundation for modern mobile apps. It is especially effective when design consistency and smooth performance are priorities. While Dart may feel unfamiliar at first and app sizes may be heavier, the overall control and freedom it offers outweigh these drawbacks.
3. Xamarin
Xamarin, owned by Microsoft, allows developers to create mobile applications using C# and .NET. It connects directly with native APIs, making the apps behave like native software.

Who It Suits
Xamarin is best suited for organizations that already use Microsoft technologies in their workflow. Development teams with knowledge of C# and .NET will find it easier to adopt without needing to learn new languages. Large companies that prioritize long-term support, security, and consistent performance often choose Xamarin. It is also a good fit for enterprise applications where stability and integration with existing systems are more important than lightweight app size.
Pros
- Strong ties to Microsoft products and tools
- High performance with results close to native apps
- One shared codebase for iOS and Android
- Good support for enterprise solutions and corporate requirements
Cons
- Produces larger app sizes compared to native mobile app development for iOS and Android
- Updates to match new versions of mobile operating systems can arrive later
- Some features may still require native coding to achieve full functionality
Xamarin is a dependable option for businesses that trust Microsoft technologies and want to keep development within a familiar environment. While it may not be the most flexible framework for smaller or highly experimental projects, it stands out for enterprise use. Its focus on security, reliability, and system integration makes it a valuable choice for companies that build large-scale applications.
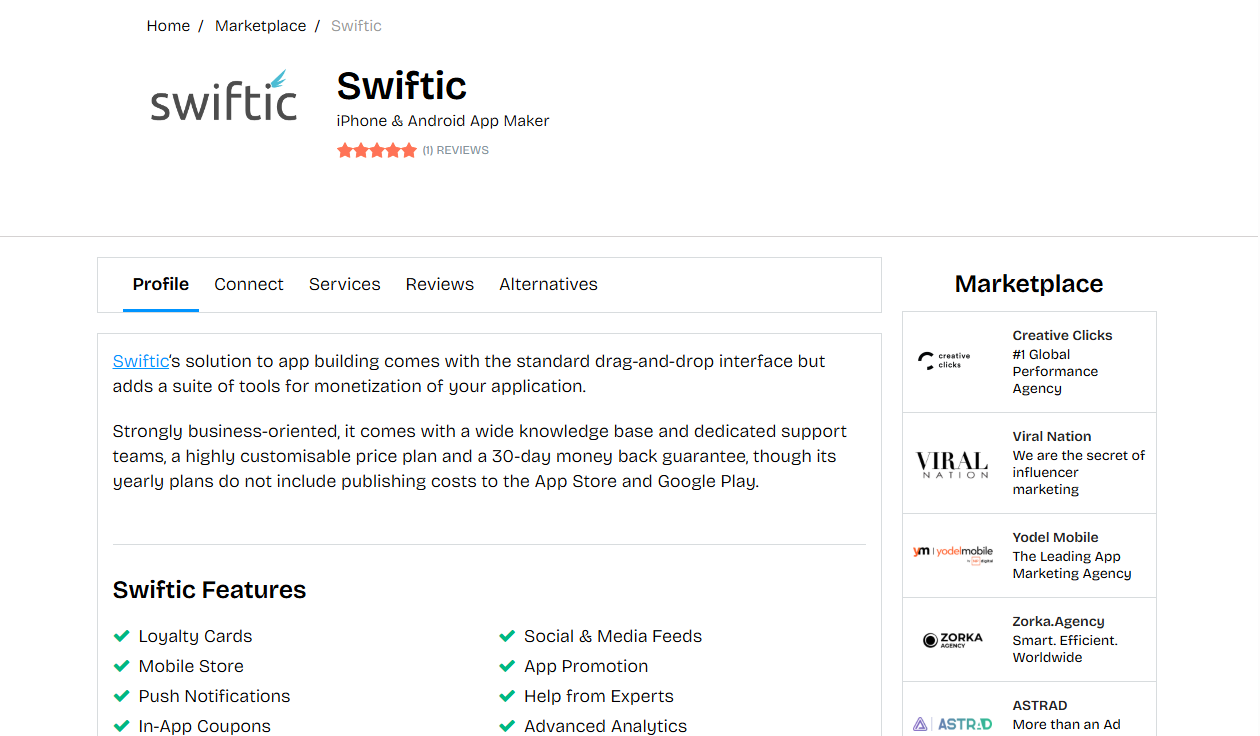
4. Swiftic
Swiftic is a mobile app platform designed mainly for small businesses that want to create apps without much technical skill. It provides an easy drag-and-drop interface and ready-made templates.
Who It Suits
Swiftic works well for shop owners, restaurants, fitness studios, and other local businesses that want to strengthen their relationship with customers. It is aimed at people who may not have a technical background but still want to offer mobile services. A business owner who needs to share promotions, accept bookings, or send updates can do this through Swiftic without hiring a development team. It is not intended for enterprise projects or apps with complex features, but for small-scale needs, it does the job.
Pros
- Easy to use, no coding knowledge required
- Templates make it possible to create an app quickly
- Comes with built-in customer engagement tools like loyalty programs
- Affordable compared to hiring professional developers
Cons
- Limited ability to create advanced or highly customized apps
- Not designed for larger companies or enterprise needs
- Customization options are more restricted than coding frameworks
Swiftic provides a straightforward way for small businesses to enter the mobile space. It may not match the flexibility of coding-based platforms, but it gives enough tools to build a functional app that serves basic business goals. For many local businesses, this balance between simplicity, speed, and cost makes Swiftic a useful solution.
5. Ionic
Ionic is a framework that uses web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build apps. It works with Angular, React, or Vue, making it flexible for developers familiar with these front-end tools.
![]()
Who It Suits
Ionic suits developers who already have experience in front-end mobile web app development and want to extend their skills into mobile. Teams that need to release apps quickly on both iOS and Android often find it a good match. It is also useful for projects where user interface design is important, since Ionic provides many pre-designed components that help create a polished look with less effort. While it may not be the first choice for apps that require high performance in gaming or graphics, it is well-suited for business apps, e-commerce, and services that rely on clear and responsive interfaces.
Pros
- Built with common web technologies that most developers already know
- One codebase can be used across multiple platforms
- Rich library of ready-to-use UI components
- Large community and a wide range of plugins for device features
Cons
- Performance is lower compared to fully native apps
- Advanced device functions may require extra coding or plugins
- Apps can become larger in size than those built with native frameworks
Ionic is a practical framework for teams with strong web backgrounds who want to enter mobile web app development without starting over. While it may not deliver the same performance as native frameworks, it covers a wide range of needs and helps deliver functional apps with appealing designs. For many businesses and developers, this balance of accessibility and flexibility makes Ionic a strong option.
6. Apache Cordova
Apache Cordova allows developers to build mobile apps using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, then wrap them for use on mobile devices. It is one of the oldest cross-platform solutions.

Who It Suits
Cordova is most suitable for teams that already have strong web development skills and want to extend their work to app development for mobile platforms. It appeals to businesses that need simple apps quickly and without large budgets. Startups or small organizations that want to test an idea before committing to a larger investment often find Cordova useful. It is not designed for projects that require high-end graphics or advanced performance, but it works well for service apps, informational apps, and prototypes.
Pros
- Straightforward for web developers to start using
- One codebase can run across multiple platforms
- Wide range of plugins available for device integration
- Open-source and free, which lowers entry costs
Cons
- Performance is weaker compared to fully native apps
- User experience may feel less natural than native applications
- Plugin support varies, and some plugins may become outdated or stop being maintained
Cordova app building platform remains a practical solution for teams that value speed and cost savings over maximum performance. While it may not compete with modern frameworks in terms of power, it still provides a reliable way to create simple, functional apps. For businesses or developers looking to reuse existing web knowledge and get an app to market quickly, Cordova continues to be a useful option.
Mobile Development Platforms Tips
Choosing the best platform for mobile app development is not only about picking a name you know. Each platform has its own way of working, and not all of them fit every project. The right choice depends on the type of app, the team’s skills, and the goals of the business. To make the decision easier, it helps to focus on a few simple points that can guide you toward mobile app development technologies that will actually support your work instead of slowing it down:
- Supported Platforms: Check if the tool covers both iOS and Android or if you will need to build separately. Cross-platform support saves time.
- Performance: Some frameworks create apps that run close to native speed, while others may feel slower. Match the platform’s ability with how demanding your app will be.
- Learning Curve: Think about the programming language used. A team skilled in JavaScript may adapt faster to React Native or Ionic, while those with C# knowledge may prefer Xamarin.
- Community and Updates: A strong developer community means more libraries, plugins, and solutions when problems appear. Look at how often the platform is updated.
- Integration Options: Consider how well the platform connects with external systems like payment gateways, APIs, or analytics tools.
- Testing and Debugging: Good built-in testing tools make the development process smoother. Without them, fixing issues can take longer.
- Cost: Some mobile application development platforms are free and open-source, while others require licenses. Budget plays a role, especially for small businesses.
No single mobile app development platform is best for every project. By looking at performance, support, and ease of use, you can match the platform with your team’s needs. Careful selection at the start often saves both time and resources later.
Back to the top
